How to Check If a Website Is Legit or a Scam?

A record $16.6 billion was made in 2025 from online scams, a 33 percent increase over 2024. As a result, website legit checkers and verification tools are becoming essential for internet usage.
A legitimate checker of websites allows you to conduct a check on the possible danger that a particular site can cause before your interaction with it, and safeguards both your personal data and financial resources. As 84 percent of individuals solicited by fake shopping sites respond to them and 47 percent lose their funds, it is no longer a choice; learning how to determine the authenticity of websites is becoming part of safe Internet browsing.
Understand the Dangers of Scam Websites
Scam websites are very dangerous sites since they are run using state-of-the-art tricks of deceit to rob people of their personal and financial details. The malicious platforms employ different approaches to disguise themselves, yet they are designed with ill intentions.
The main risks are:
- Identity Theft and Financial Fraud: Scammers can design false websites and gather the username, password, credit card details, and personal data. Loss of money due to online scams involving fake websites is the most common type of online fraud, with a rate of 36.7% of global online shoppers falling victim to this scam.
- Malware Distribution: Fake websites are often used to distribute malicious programs, which include viruses, ransomware, and spyware that may attack your machine and steal valuable information.
- Phishing Attacks: It is a fraudulent technique by which scammers pretend to be credible companies, the government, or financial organizations to lure users into learning classified information. These attacks have also become trickier and involve clones of well-known sites.
Scam websites appeal to human psychology using a sense of urgency, excitement, and fear, and bypass your protective instincts to make hurried decisions.
The financial loss is immense. In 2025, the FTC reported that consumers suffered losses exceeding $12.5 billion as a result of fraud, reflecting a 25 percent rise compared to the previous year. The first step in preventing yourself from becoming a statistic is realizing these risks.
Use a Website Scam Tester Tool
Website scam tester tools provide automated analysis of potentially dangerous websites, offering quick assessments before you engage with unfamiliar sites. These tools scan various website elements to identify red flags and security vulnerabilities.
Popular Website Scam Tester Tools:
| Tool | Key Features | Best For |
| ScamAdviser | Domain analysis, trust score, customer reviews | General website verification |
| Bitdefender Link Checker | Real-time scanning, malware detection | Security-focused analysis |
| McAfee SiteAdvisor | Integrated browser protection, reputation scoring | Ongoing browsing protection |
| Norton Safe Web | Comprehensive threat detection, community ratings | All-around safety assessment |
How to Use These Tools:
- Copy the suspicious website URL
- Paste it into the scam tester tool
- Review the generated safety report
- Check trust scores and identify risks
- Read user reviews and complaints
Such tools examine details about domain registers, SSL certificates, the reputation of sites, and common threat databases to deliver a full safety evaluation. It must be noted that none of the tools is 100 percent accurate, but they can give an idea about the existing possible risks.
Test the Website Design and Content Red Flags
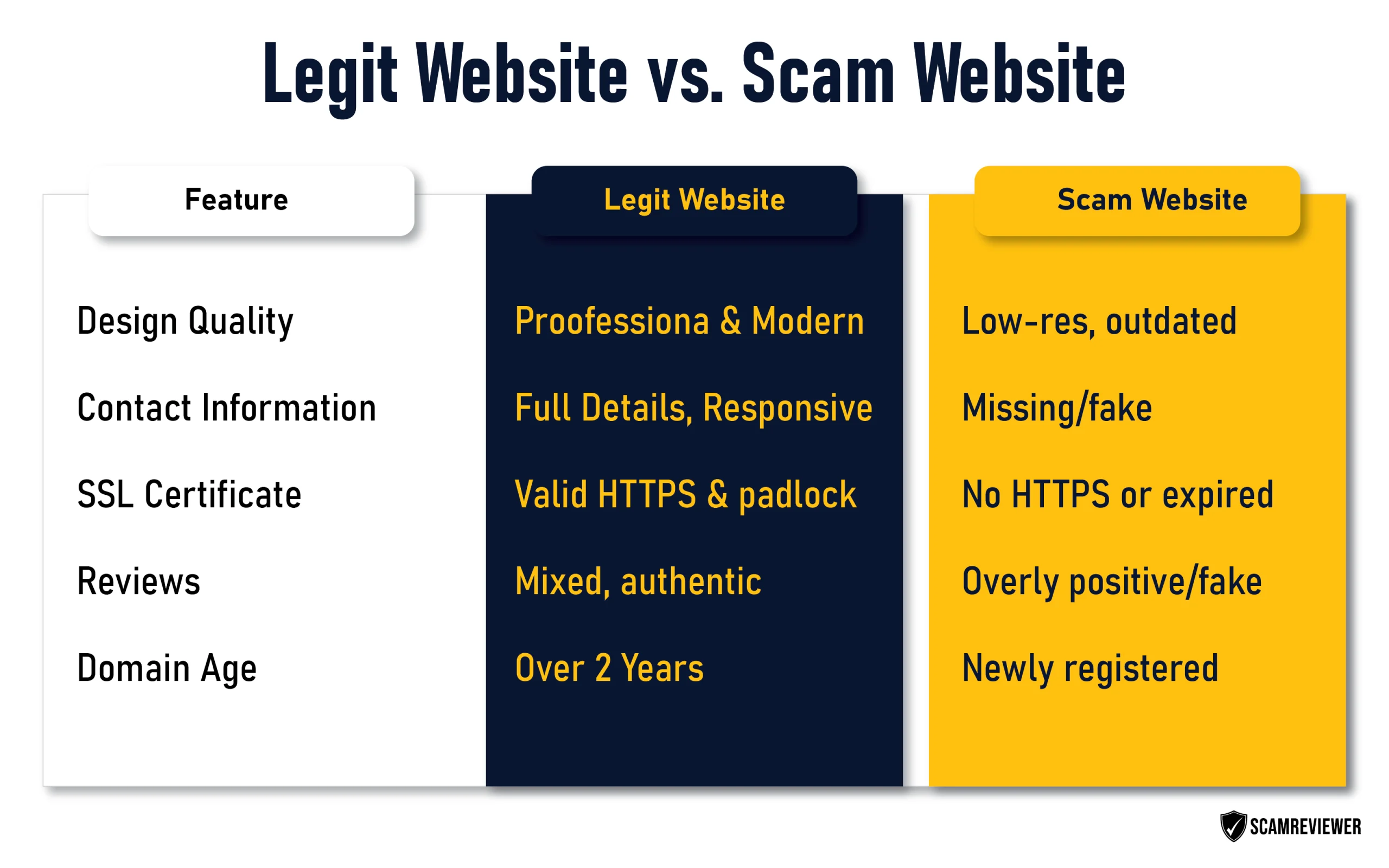
Generally speaking, the legitimacy of a website can be determined by its design and content quality. Quality web design is an investment that professional businesses make, and scammers often set up sites that are poorly put together, and their flaws are easy to identify.
Safe Website Structure Indicators:
Professional Design Elements:
- Clean, modern layout with consistent branding
- High-quality images and graphics
- Professional typography and color schemes
- Mobile-responsive design
- Fast loading times
Quality Content Markers:
- Proper grammar and spelling throughout
- Comprehensive product or service descriptions
- Regular content updates and fresh information
- Clear navigation and site structure
- Professional photography and media
Red Flags to Watch For:
Poor Design Quality:
- Outdated or amateur-looking layouts
- Pixelated or low-resolution images
- Inconsistent fonts and colors
- Broken links or missing pages
- Pop-up advertisements and intrusive elements
Content Warning Signs:
- Spelling and grammatical errors
- Overly promotional or sensationalized language
- Missing or incomplete information
- Copied content from other websites
- Unrealistic claims or promises
Suspicious Elements:
- Urgent countdown timers create false pressure
- Unrealistic offers and pricing
- Lack of detailed contact information
- No clear return or refund policies
- Requests for unnecessary personal information
Remember that legitimate businesses maintain professional standards across all aspects of their online presence. If a website looks unprofessional or contains obvious errors, proceed with extreme caution.
Use a Legit Website Checker to Verify Safety
Multiple verification tools and methods can help confirm a website’s legitimacy. Using various approaches provides comprehensive protection against sophisticated scams.
Essential Verification Tools:
Trust and Safety Platforms:
- Trustpilot: Customer reviews and business ratings
- Better Business Bureau: Accredited business verification
- Sitejabber: User-generated reviews and ratings
- Scamwatch: Government-backed scam reporting database
Technical Verification Tools:
- VirusTotal: Multi-engine malware scanning
- URLVoid: Reputation checking across multiple databases
- Web of Trust (WOT): Community-driven safety ratings
- Google Safe Browsing: Integrated browser protection
Multi-Layer Verification Process:
- Run automated scans using multiple tools
- Cross-reference results across different platforms
- Check for consistent information across verification sources
- Look for recent reviews and user experiences
- Verify business registration and licensing when applicable
Key Verification Checkpoints:
- Domain reputation across security databases
- SSL certificate validity and encryption status
- Contact information verification and business registration
- Payment method security and processing standards
- User review authenticity and complaint patterns
Using multiple verification methods provides layered protection against sophisticated scams that might fool individual tools.
Look for Contact Information, Reviews, and Social Proof
Legitimate businesses provide comprehensive contact information and maintain transparent communication channels. The absence of clear contact details or social proof is a major red flag.
Essential Contact Information:
Required Contact Elements:
- Physical business address (not just P.O. Box)
- Multiple contact methods (phone, email, chat)
- Customer service hours and response times
- Professional email addresses (not free providers)
- Clear contact forms with proper functionality
Social Proof Indicators:
- Verified social media profiles with regular activity
- Customer testimonials with names and photos
- Third-party review platforms presence
- Industry certifications and accreditations
- Media mentions and press coverage
Verification Methods:
Contact Information Testing:
- During business hours, call the numbers provided
- Send test emails to verify response times
- Check if physical addresses exist using maps
- Verify that social media profiles are active and legitimate
- Look for consistent information across platforms
Review Analysis:
- Read both positive and negative reviews
- Check review dates and frequency patterns
- Look for detailed, specific feedback
- Verify that reviewer profiles aren’t fake
- Cross-reference reviews across multiple platforms
Warning Signs:
- Only generic contact forms are available
- No phone number or unresponsive lines
- Fake or non-existent business addresses
- Reviews that seem artificial or overly positive
- No presence on major social media platforms
- Unwillingness to provide detailed information
Legitimate businesses are transparent about their operations and welcome customer communication. If a company seems evasive or provides limited contact options, exercise extreme caution.
Check Website Security Certificates (HTTPS, SSL)
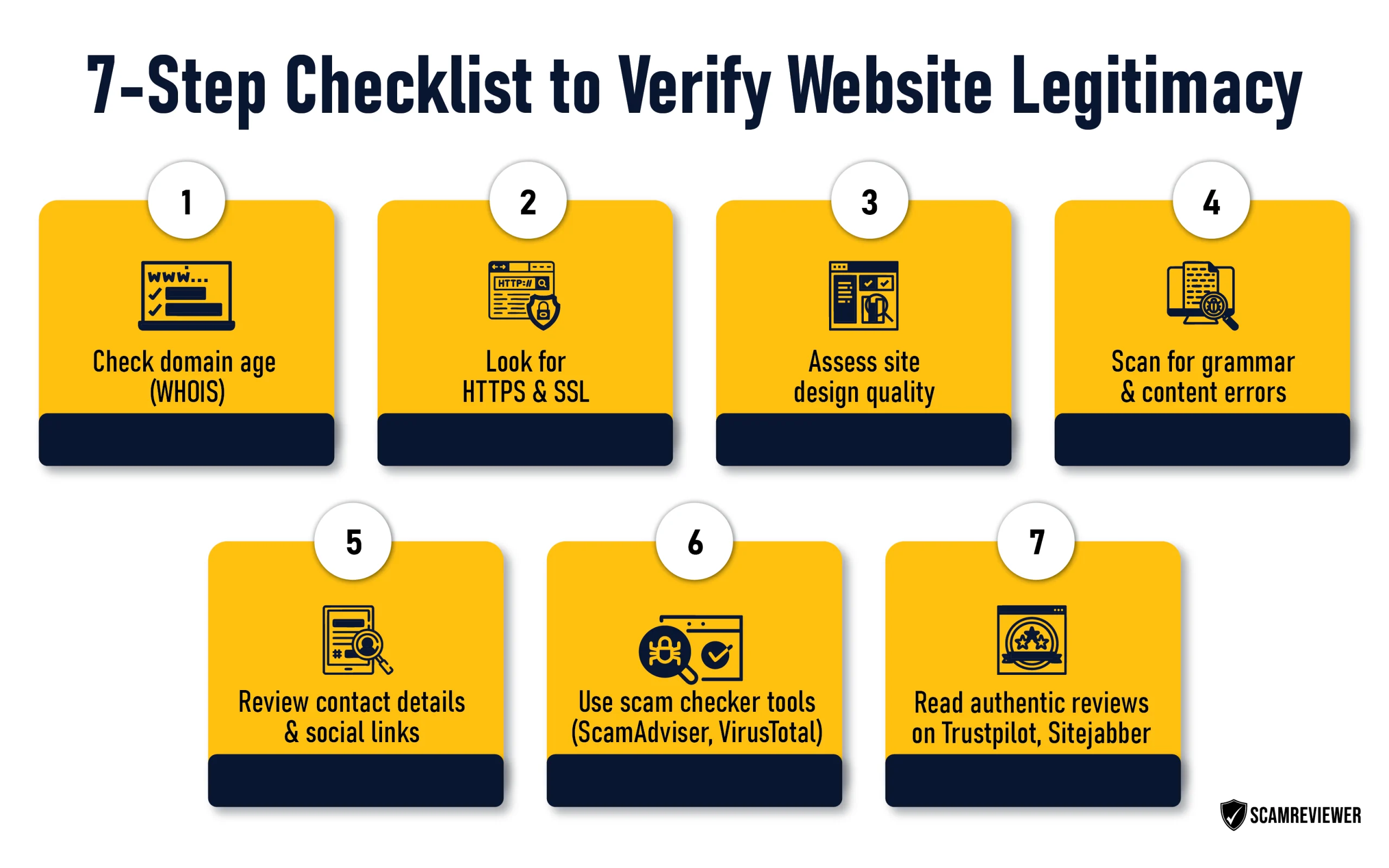
Website security certificates are fundamental indicators of legitimacy and data protection. Understanding how to verify these certificates helps identify secure connections and potential threats.
Understanding SSL/HTTPS:
What to Look For:
- HTTPS prefix in the URL (not just HTTP)
- Padlock icon in the browser address bar
- Green address bar indicating extended validation
- Valid certificate details when clicked
- Certificate authority verification from trusted providers
Certificate Verification Process:
- In your browser’s address bar, look for the padlock icon
- Click on the certificate to view detailed information
- Confirm the legitimacy of the certificate issuer
- Check expiration dates and validity periods
- Ensure the certificate matches the website domain
Security Certificate Types:
| Certificate Type | Security Level | Verification Process |
| Domain Validated (DV) | Basic | Minimal verification |
| Organization Validated (OV) | Enhanced | Business verification |
| Extended Validation (EV) | Highest | Comprehensive verification |
Red Flags:
Certificate Warning Signs:
- Browser security warnings about certificates
- Self-signed certificates from unknown authorities
- Expired or invalid certificates
- Certificate domain mismatches
- Mixed content warnings (HTTPS and HTTP)
Additional Security Checks:
- Verify the certificate covers all subdomains
- Check for certificate transparency logs
- Look for HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
- Ensure proper certificate chain validation
- Verify certificate revocation status
Remember that while HTTPS is essential, it doesn’t guarantee a website is legitimate—scammers can also obtain SSL certificates. Make use of this as one component in your overall evaluation.
Use WHOIS Lookup and Domain Age Check
Domain registration information provides valuable insights into website legitimacy and ownership history. WHOIS lookups and domain age analysis can reveal important details about a site’s background.
WHOIS Lookup Process:
Essential Information to Check:
- Domain registration date and age
- Registrant contact information and location
- Domain expiration date and renewal history
- Registrar information and reputation
- Administrative and technical contacts
Domain Age Analysis:
Legitimate Website Indicators:
- Domains registered for multiple years
- Consistent registration renewal patterns
- Stable registrant information over time
- Professional registrar services
- Realistic registration locations
Suspicious Patterns:
- Very recent domain registrations
- Domains registered for short periods
- Frequently changing registrant information
- Privacy protection hides all details
- Bulk registrations from the same entity
Using WHOIS Tools:
Popular WHOIS Services:
- WHOIS.net: Comprehensive domain information
- Domain Tools: Professional domain analysis
- ICANN WHOIS: Official domain registry data
- Who is: User-friendly interface and analysis
- Whois.com: Detailed domain history
Interpretation Guidelines:
Positive Indicators:
- Domains older than 2-3 years
- Consistent contact information
- Professional business registration
- Realistic geographical locations
- Proper DNS configuration
Warning Signs:
- Domains registered within the last few months
- Complete privacy protection, masking all details
- Suspicious or non-existent contact information
- Bulk registrations with similar patterns
- Frequent changes in registration details
While privacy protection is legitimate for personal websites, businesses should provide verifiable contact information. Domain age should be one component of your overall evaluation, not the only one.
Final Thoughts
To defend yourself against scam sites, you should have caution, the necessary tools, and a properly organized process of checking. As online fraud losses continue to reach unprecedented levels, individuals should establish these skills to browse the internet safely.
Always check with more than one method available to know if a company is legit, follow your intuition, or if you feel anything is suspiciously wrong, and do not act in a hurry. The amount of time that one takes to validate that a particular site is legitimate is minuscule compared to the possible effects of being a victim.
Have a nose for new threats, employ reliable security software, and display a natural degree of suspicion when visiting unknown websites. These precautionary steps determine your digital security.
What are the common signs of a fake website?
Fake websites often exhibit several telltale signs:
Design and Content Red Flags:
- Poor grammar and spelling errors
- Low-quality or stolen images
- Unprofessional layout and design
- Broken links and missing pages
- Excessive pop-ups and advertisements
Technical Warning Signs:
- No HTTPS encryption or security certificates
- Suspicious URL variations of legitimate sites
- Missing contact information or fake addresses
- No customer reviews or testimonials
- Expensive or unrealistic packages
Behavioral Indicators:
- Pressure tactics and urgent countdown timers
- Requests for unnecessary personal information
- Limited payment options or unusual payment methods
- No clear return or refund policies
- Lack of social media presence or verification
If something feels wrong, it probably is; trust your instincts. Legitimate businesses invest in professional web presence and transparent communication.
Is it safe to enter personal info on unfamiliar websites?
No, entering personal information on unfamiliar websites carries significant risks and should be avoided until you've thoroughly verified the site's legitimacy.
Before Sharing Any Information:
- Verify the website using multiple scam checker tools
- Confirm HTTPS encryption and valid SSL certificates
- Verify the validity of the company registration and contact details
- Read customer reviews and check business ratings
- Visit the company's social media accounts and other online presences
Information to Never Share:
- Social Security Numbers or national ID numbers
- Full banking details or account numbers
- Passwords or security question answers
- Copies of official documents (unless a verified necessity)
- Personal information beyond what's necessary
Safe Sharing Practices:
- Use temporary or disposable email addresses for initial contact
- Provide minimal information required for the specific transaction
- Monitor your accounts after sharing any information
- Use secure payment methods like credit cards (not debit cards)
- Keep records of all interactions and transactions
When in doubt, contact the company through official channels to verify their legitimacy before sharing any personal information.
What should I do if I find a scam website?
If you discover a scam website, take immediate action to protect yourself and others:
Immediate Actions:
- Stop all interaction with the website immediately and check the scam website
- Don't download anything or provide additional information
- Screenshot the website for evidence before it potentially disappears
- Check your accounts for any unauthorized activity
- Change passwords if you've shared any login credentials
If You've Already Shared Information:
- Cancel compromised credit cards immediately
- Monitor bank statements for unauthorized transactions
- Place fraud alerts on your credit reports
- Update passwords for all important accounts
- Contact your bank to report potential fraud
Report the Scam:
- FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3): www.ic3.gov
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): reportfraud.ftc.gov
- Google Safe Browsing: Report phishing sites
- Your local police: For significant financial losses
- Anti-phishing organizations: Such as PhishTank.org
Help Others:
- Post reviews on scam databases and consumer protection sites
- Use community forums and social media to spread cautions
- Report to the relevant authorities in your jurisdiction
- Notify the legitimate company if the scam impersonates them
Quick action can minimize damage and help prevent others from falling victim to the same scam.
