What are Neobanks: Are they Safe? How do Neobanks differ from Traditional Banks?

Traditional banking is evolving to meet the needs of modern consumers in today’s fast-paced digital world. Customers are now looking for banking solutions that are faster, more versatile, and more cost-effective due to the evolution of fintech innovations. Neobanks, a new type of digital financial institution built to simplify banking, has surfaced as a response to this development.
Understanding Neobanks: The Future of Digital Banking
Neobanks also called Challenger Banks, are digital-only banks offering a seamless online banking experience and no physical branches. Neobanks, unlike conventional banks, employ technology to provide banking services that are faster, cheaper, and simpler to use.
Neobanking platforms provide features like integrated budgeting tools, AI-driven financial insights, no hidden fees, and quick account registration. They serve tech-savvy consumers, independent contractors, and companies seeking effective banking solutions that prioritize mobile devices.
With no physical presence, neobanks reduce operational costs, passing the benefits on to customers through higher interest rates and lower fees. Neobanking is poised to transform the banking industry and make financial management easier and more accessible as digital finance expands.
Swipe Through Time: The Evolution of neo banks
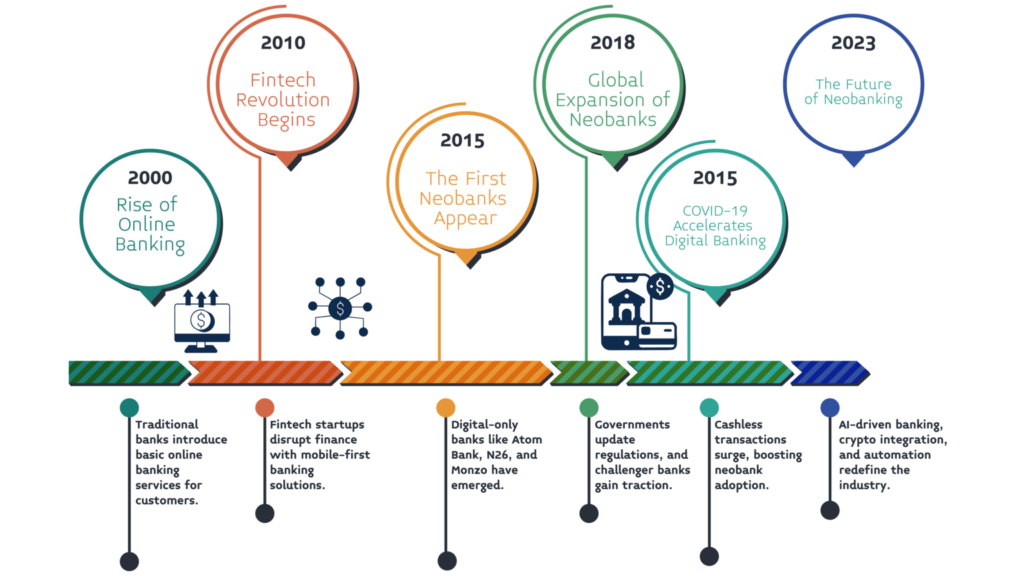
How do Neobanks work?
Neobanks are online-only fintech banks that provide a smooth neobanking experience without the need for physical locations. To deliver effective and affordable financial services, they make use of state-of-the-art technology, automation powered by AI, and mobile-first solutions.
Neobanks, as opposed to traditional banks, provide services by partnering with approved financial institutions or obtaining their banking licenses. This is how they work:
- Fully Digital Infrastructure:
No physical branches; everything is managed via mobile apps and websites. - Instant Account Opening:
Customers can sign up in minutes with minimal paperwork. - AI & Automation:
AI-driven tools manage transactions, budgeting, and expense tracking. - Lower Fees & Higher Savings:
With no physical infrastructure, fintech banks offer lower fees and better interest rates. - Smart Financial Insights:
Automated analytics help users optimize spending and investments. - Seamless Payments & Transfers:
Integrated payment solutions enable quick P2P transfers, bill payments, and global transactions. - Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS):
Many neobanks provide API-driven solutions for businesses to integrate banking features.
Who can use Neobanks?
Neobanks are designed to cater to a wide range of users who seek convenience, lower fees, and tech-driven banking solutions. Unlike traditional banks, neobanks offer a fully digital experience, making them ideal for various customer segments.
Neobanks Are Perfect for These Users:
- Tech-Savvy Individuals:
People who prefer mobile banking and digital transactions over traditional banking. - Freelancers & Gig Workers:
Neobanks provides easy account management, invoicing, and real-time payments, perfect for those with irregular incomes. - Small Business Owners & Startups:
Many FinTech banks offer business banking solutions, including expense tracking and seamless payment integration. - Frequent Travelers & Expats:
With low foreign exchange fees, multi-currency accounts, and global payment options, neobanks are great for those on the move. - Students & Young Professionals:
Neobanks offers budgeting tools, no-minimum balance accounts, and better savings options for young users. - Underbanked & Unbanked Individuals:
For those without easy access to traditional banking, neobanks offer hassle-free financial inclusion with online KYC verification.
Are Neobanks Safe?
Many consumers are wondering, “Are neobanks safe?” as digital banking becomes more popular. Neobanks’ security measures are dependent on technology, encryption, and regulatory compliance because they don’t have any physical branches.
How Safe Are Neobanks?
- Regulated by Financial Authorities:
Most neobanks operate under strict financial regulations by partnering with licensed institutions or obtaining independent banking licenses. - Advanced Security Measures:
Neobanks uses end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication (2FA), and biometric security to protect user accounts. - Deposit Protection:
Some neobanks are covered under deposit insurance programs, ensuring customer funds are safeguarded. - Fraud Detection & AI Monitoring:
AI-driven security tools help detect suspicious activities and prevent fraud in real time. - No Physical Branches, Lower Risks:
Without branch-based vulnerabilities like check fraud or physical theft, neobanks eliminate many traditional security concerns.
Things to Consider Before Using a Neobank
- Check for Licensing & Regulatory Compliance – Always ensure the neobank is registered with financial authorities in your country.
- Review Security Features – Look for biometric logins, fraud alerts, and multi-layer encryption.
- Understand Fund Protection Policies – Not all neobanks offer deposit insurance, so verify before depositing large sums.
So, are neobanks safe? Yes, when they are regulated, encrypted, and follow best security practices. However, customers must stay informed and choose reputable neobanks for secure digital banking.
The Rise of Neobanks
Neobanks are redefining the financial industry by leveraging technology, meeting evolving customer expectations, and adapting to regulatory changes. These digital only banks offer cost-effective solutions, cater to niche audiences, and scale rapidly disrupting traditional banking and reshaping the financial landscape.
Key Drivers Behind Neobank Growth
1. Technological Advancements
Neobanks thrive on cutting-edge technology. Mobile banking, cloud computing, and AI-driven financial solutions provide seamless, secure, and accessible banking experiences. Additionally, advancements in cybersecurity have strengthened trust in digital banking, ensuring safe transactions and data protection.
2. Evolving Customer Expectations
Modern consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, demand fast, personalized, and convenient banking services. Neobanks cater to these needs with:
- 24/7 digital access via smartphones and computers
- User-friendly interfaces and real-time notifications
- AI-powered financial advice and spending insights
3. Regulatory Changes Encouraging Competition
Government policies worldwide are fostering a competitive banking environment. For example, Europe’s revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) allows third-party providers to access bank data, enabling neobanks to offer more innovative financial products. Similar regulations in other regions are encouraging new entrants, further driving neobank expansion.
4. Cost Efficiency & Competitive Pricing
Unlike traditional banks, neobanks operate without physical branches, significantly reducing overhead costs. This allows them to:
- Offer lower fees and higher interest rates
- Provide affordable banking services to underserved populations
- Scale their business more efficiently
5. Targeting Niche Markets
Neobanks differentiate themselves by catering to specific customer segments, such as:
- Freelancers and gig workers
- Expatriates and digital nomads
- Individuals in remote or underbanked areas
With innovative products and aggressive digital marketing strategies, neobanks are rapidly growing and capturing market share.
6. Global Scalability & Expansion
Neobanks are not confined by physical locations, enabling them to expand globally with minimal investment. Their digital-first approach allows them to enter new markets swiftly, making financial services more accessible worldwide.
How are Neo-Banks changing banking forever?
- The rise of neobanks and its impact on traditional banks is revolutionizing the financial industry.
- Neobanks offers fully digital banking with lower fees, AI-driven insights, and seamless mobile experiences.
- Unlike traditional banks, neobanking eliminates physical branches, reducing operational costs and allowing competitive interest rates.
- Neobanks cater to niche markets, such as freelancers, digital nomads, and underbanked populations.
- Their innovative approach forces traditional banks to modernize or risk obsolescence.
- As neobanks continue to grow, they are redefining banking, making financial services more accessible, efficient, and customer-focused worldwide.
Traditional Banks Vs Neobanks
The following table contains key differences between Traditional Banks and Neobanks:
|
Features |
Traditional Banks |
Neobanks |
| Physical Presence | Operate through branches | 100% digital, no physical branches |
| Cost Efficiency | High operational costs due to infrastructure | Lower costs due to the digital-only model |
| Customer Convenience | Limited banking hours, and in-person visits required | 24/7 access via mobile apps & online banking |
| Technology Integration | Slow adoption of digital tools | AI-driven, cloud-based, and tech-first approach |
| Speed of Transactions | Often slower due to legacy systems | Instant transfers, real-time notifications |
| Personalization | Generalized banking solutions | AI-powered insights, customized financial tools |
| Target Audience | Mass-market, corporate clients | Niche markets (freelancers, digital nomads, underbanked) |
| Fees & Interest Rates | Higher fees and lower interest on savings | Lower fees, better interest rates |
| Regulatory Framework | Heavily regulated with strict compliance | Often operate under fintech regulations, more flexible |
| Global Scalability | Requires physical expansion, high costs | Can scale globally with minimal investment |
Advantage of Neobanks
- Lower Fees & Cost Efficiency:
Neobanks operate without physical branches, significantly reducing overhead costs. This allows them to offer lower fees and better interest rates compared to traditional banks. - 24/7 Digital Access:
Unlike traditional banks, neobanking offers round-the-clock access through mobile apps and online platforms, ensuring convenience. - AI-Driven Personalization:
Fintech banks leverage AI and big data to provide tailored financial insights, budgeting tools, and spending analytics. - Faster Transactions:
Neobanks process payments instantly, eliminating delays often seen in traditional banking systems. - Global Scalability:
Without physical limitations, neobanks can expand quickly across borders, offering financial services to a broader audience. - Niche Market Focus:
Many fintech banks cater to underserved segments such as freelancers, gig workers, and digital nomads with specialized banking solutions. - User-Friendly Experience:
Intuitive mobile interfaces and seamless integration with financial apps make neobanking highly appealing to tech-savvy users. - Paperless & Eco-Friendly:
Fully digital processes reduce paperwork, making neobanks a more sustainable banking option.
Neobank Disadvantages
- Limited Physical Support:
Unlike traditional banks, neobanks lack physical branches, making in-person customer support unavailable. - Regulatory Uncertainty:
Fintech banks often operate under evolving financial regulations, leading to potential compliance issues. - Security & Fraud Risks:
The rise in banking scams like new banking scams using reverse instant payments has increased concerns about digital banking security. Instant payments banking scam is one such emerging threat that highlights the vulnerabilities in digital transactions. - Limited Financial Products:
While traditional banks offer comprehensive services (loans, mortgages, investments), some neobanks provide only basic banking solutions. - Dependence on Technology:
Neobanking relies heavily on mobile apps and cloud systems, making users vulnerable to outages and cybersecurity threats. - Trust Issues Among Older Generations:
Many customers still prefer traditional banks due to their long-standing reputation and physical presence. - No Cash Deposit Option:
Since neobanks operate digitally, users may find it difficult to deposit cash without relying on third-party services. - Potential Account Freezes:
Due to automated fraud detection, some fintech banks may freeze accounts without human intervention, causing inconvenience to users.
Regulatory Considerations of Neobanks
As of 2025, neobanks face several regulatory considerations:
- Licensing and Regulatory Frameworks:
In many jurisdictions, neobanks operate without full banking licenses, often partnering with traditional banks to offer services. This model requires adherence to complex regulatory environments, including compliance with central bank guidelines and financial regulations. - Data Privacy and Cybersecurity:
With the rise of digital banking, regulatory bodies emphasize robust data protection and cybersecurity measures. Neobanks must implement advanced security protocols to protect customer data and comply with data privacy laws. - Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance:
Neobanks are required to establish stringent AML and KYC processes to prevent financial crimes. This includes continuous monitoring, regular audits, and ensuring that customer verification processes meet regulatory standards. - Capital Adequacy and Liquidity Requirements:
Regulators may impose specific capital and liquidity requirements on neobanks to ensure financial stability. For instance, the Reserve Bank of India has proposed additional liquidity buffers for digitally accessible deposits to mitigate rapid withdrawal risks. - Consumer Protection and Dispute Resolution:
Ensuring consumer protection is paramount. Neobanks must establish effective grievance redressal mechanisms and transparent communication channels to address customer complaints promptly. - Operational Resilience and Technology Risk Management:
Given their reliance on technology, neobanks must demonstrate robust operational resilience. This includes having contingency plans for system outages, regular stress testing, and compliance with technology risk management guidelines. - Collaboration with Traditional Banks:
In regions where neobanks lack direct regulatory recognition, they often collaborate with traditional banks. These partnerships necessitate clear agreements outlining responsibilities, compliance obligations, and risk management practices.
Conclusion
Neobanks are revolutionizing the financial industry with fully digital, AI-powered, and cost-effective banking solutions. Their rise has challenged traditional banks, pushing them to adopt digital-first strategies.
By eliminating physical branches, neobanking offers lower fees, instant transactions, and personalized financial tools, making banking more accessible.
However, challenges like regulatory compliance, cybersecurity risks, and trust issues remain. As fintech banks evolve with AI, blockchain, and open banking, they will continue reshaping global finance.
While neobanks provide convenience and efficiency, customers must choose reputable providers and prioritize security. The future of banking is digital, and neobanks are leading the transformation.
